Calcium Carbonate (chemical formula: CaCO₃) is a non-toxic, odorless, and tasteless inorganic compound, commonly known as chalk, limestone, calcite, or marble. It is one of the most common minerals on Earth, widely found in natural rocks (such as limestone and marble) and in biological skeletons and shells. Calcium carbonate is categorized into three main types: Precipitated Calcium Carbonate (PCC), Ground Calcium Carbonate (GCC), and Nano Calcium Carbonate (NPCC). Below, we will explore their differences and how to make the right choice.
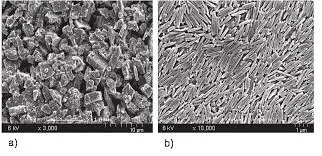
Precipitated Calcium Carbonate, PCC

Process: Produced by calcining limestone, hydrating it with water to create milk of lime, and then precipitating it by introducing carbon dioxide gas.
Particle Morphology: Regular crystal shapes (e.g., spindle, cubic, needle-like), with uniform particle size distribution.
Particle Size Range: Relatively fine, typically in the micrometer range (e.g., 1μm ~ 3μm).
Specific Surface Area: Medium
Key Characteristics: High purity, uniform particle size, low oil absorption.
Ground Calcium Carbonate, GCC

Process: Produced by mechanically crushing, grinding, and classifying natural minerals (such as calcite, marble).
Particle Morphology: Irregular fragments, multi-edged, with a relatively wide particle size distribution.
Particle Size Range: Relatively coarse, typically in the micrometer range (e.g., 325 mesh ~ 2500 mesh, approximately 45μm ~ 5μm).
Specific Surface Area: Small
Key Characteristics: Low cost, low processing energy consumption, stable properties.
Nano Calcium Carbonate (NPCC)

Process: Based on the light calcium process, produced by controlling crystallization conditions and adding crystal shape guides and surface treatment agents.
Particle Morphology: More regular crystal shapes, reaching nanoscale (1-100nm), but particles typically agglomerate into micrometer-sized clusters.
Particle Size Range: Nanoscale (primary particles are 1-100nm).
Specific Surface Area: Very large
Key Characteristics: Surface effects, small size effects, functional properties, requires surface treatment to prevent agglomeration.
So, after understanding their differences, how should you choose among them?
Plastics Industry

Ground Calcium Carbonate (GCC): Serves as a low-cost filler, primarily increasing product volume and significantly reducing raw material costs. Used extensively in PVC products with lower mechanical performance requirements, like ordinary drainage pipes, flooring substrates, and sheets. Its lower oil absorption helps reduce plasticizer usage in formulations. Effect: Cost reduction, but decreases impact strength and tensile strength.
Precipitated Calcium Carbonate (PCC): Acts as a functional filler, reducing costs while also improving the physical properties of products. Used in high-grade PVC profiles, pipes, artificial leather, and footwear materials. Its regular spindle-shaped structure enhances product gloss, dimensional stability, stiffness, and thermoplasticity. Effect: A cost-effective choice, significantly improving product appearance and some mechanical properties without a substantial cost increase.
Nano Calcium Carbonate (NPCC): Functions as a functional enhancer. The main goal is not cost reduction but imparting exceptional properties to the plastic matrix. Used in automotive plastic parts, super-tough nylon, high-grade sealing strips, and engineering plastics. Due to its nano-size effects, it reinforces, toughens, and provides anti-aging properties. Effect: Can simultaneously increase material stiffness and toughness, but is expensive and requires surface treatment for uniform dispersion.
Paper Industry

Ground Calcium Carbonate (GCC): Used as a common filler and coating pigment. Used as a filler in cultural paper and as a coating for mid-to-low-grade coated paper and board. Effect: Improves paper whiteness and opacity, reduces costs. However, its irregular particles offer limited improvement in paper smoothness and gloss.
Precipitated Calcium Carbonate (PCC): Serves as a high-grade filler and coating pigment. Primarily used in high-quality art paper, digital photo paper, etc. Its regular crystal shapes (e.g., spindle, rhombic) form a superior microstructure. Effect: Greatly enhances coated paper smoothness, gloss, ink absorption, and printability, resulting in paper with a good feel and vibrant printed images.
Nano Calcium Carbonate (NPCC): Acts as a special functional additive. Used in specialty papers requiring specific properties, such as high-gloss ink-absorbent paper or high-barrier packaging paper. Effect: Leverages its huge specific surface area to achieve ultra-high gloss, opacity, or specific pore structures.
Coatings and Paints Industry

Ground Calcium Carbonate (GCC): Functions as an extender pigment (bulking agent). Mainly used in interior wall emulsions and primers requiring high filler loadings. Effect: Increases film thickness, enhances hiding power, and significantly reduces raw material costs.
Precipitated Calcium Carbonate (PCC): Serves as a functional filler. Used in high-grade interior paints, industrial paints, and solvent-based paints requiring surface smoothness and gloss. Effect: Its regular particles help improve paint film smoothness, gloss, and leveling, while enhancing scrub resistance.
Nano Calcium Carbonate (NPCC): Acts as a functional additive. Used in high-end automotive paints, anti-corrosion coatings, UV-curable coatings, etc. Effect: Provides thixotropy (anti-sagging), enhances film strength, wear resistance, and anti-aging properties.
Rubber and Adhesives Industry

• In Rubber:
◦ Ground Calcium Carbonate is used for filling low-grade products.
◦ Light Calcium Carbonate provides some semi-reinforcing effects.
◦ Nano Calcium Carbonate is a key reinforcing material used in tire sidewalls, inner tubes, and high-grade rubber products, significantly improving tensile strength, tear strength, and abrasion resistance.
• In Adhesives and Sealants:
◦ Light Calcium Carbonate is the primary filler, serving three purposes: thickening, reinforcing, and cost reduction.
◦ Nano Calcium Carbonate is used in high-performance products. In addition to reinforcement, it effectively controls the product’s rheology, preventing sagging during application on vertical surfaces.

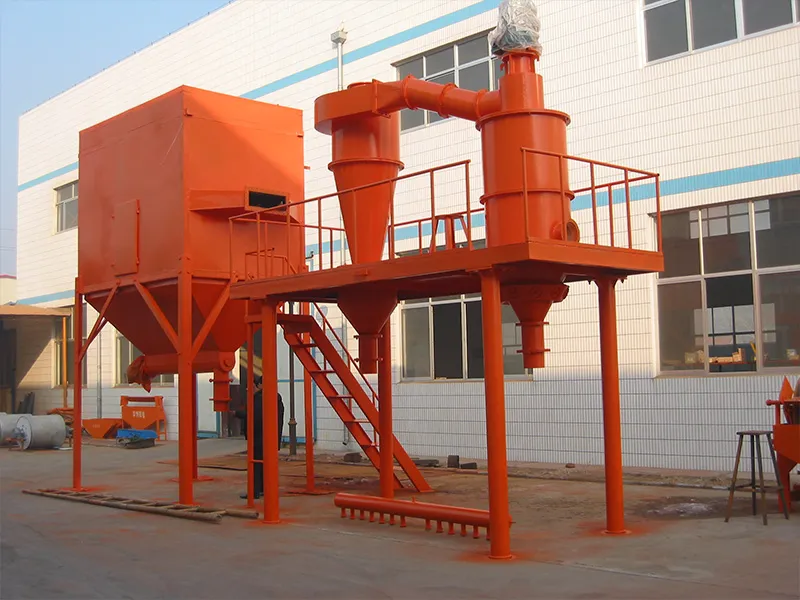
Epic Powder Machinery: Your Partner in Precision Grinding
Choosing the right calcium carbonate is crucial for your product’s performance. Equally important is having reliable equipment to achieve the desired particle size and distribution for your specific application. 艾匹克粉末機械 specializes in advanced classifying mills and powder processing solutions. Our machinery is engineered for high precision, efficiency, and stability, helping you produce high-quality GCC, PCC, and even handle demanding nano-scale applications effectively. Trust Epic to deliver the grinding technology that empowers your materials to perform.

