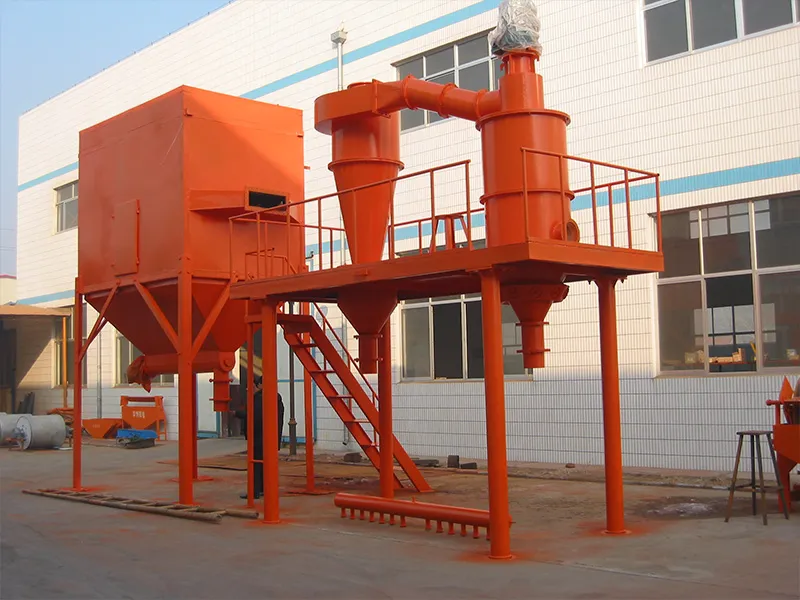
Classifying equipment for metallic ultra-fine spherical powders plays a crucial role in accurately separating powders by particle size. The goal is to achieve precise classification while maintaining the powders’ sphericity and particle size distribution to meet the demands of advanced applications. Several types of classifying equipment are commonly used, each with distinct principles and advantages.

Air Classifier
The Air Classifier operates by generating centrifugal force through high-speed airflow within the classification chamber, separating powders by size. It offers high precision for micron-level ultra-fine powders and is well-suited for easily oxidizable or flammable metals like aluminum and magnesium, especially when equipped with inert gas protection systems. This equipment features a compact design, high processing capacity, and low energy consumption, making it popular in industries such as lithium battery cathodes, 3D printing metal powders, and glass powder production.
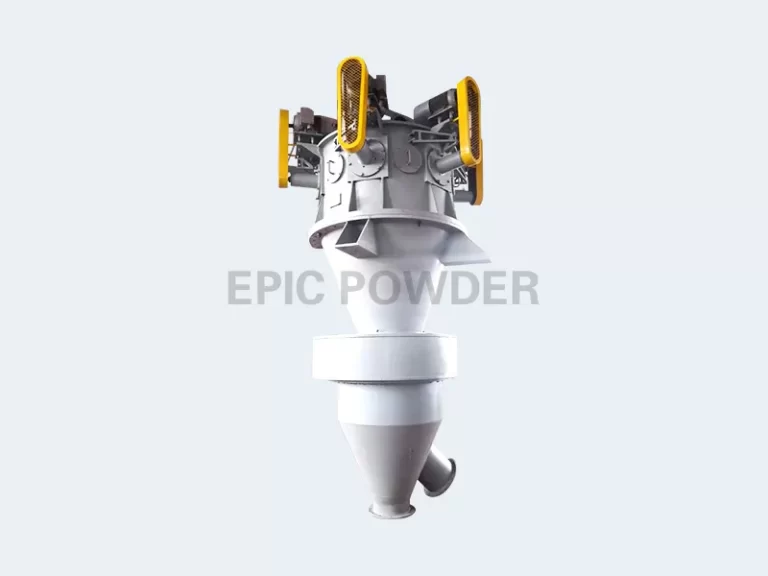

Turbo Classifier
The Turbo Classifier works using rapidly rotating turbine blades that produce centrifugal force, stratifying powders within the chamber. It provides high classification efficiency along with multi-stage grading capabilities, delivering a narrow particle size distribution and excellent sphericity. With compatibility for online particle size detection systems, turbo classifiers allow real-time adjustments during processing. Typical applications include aerospace-grade metal powders, catalyst carriers, and ceramic materials.
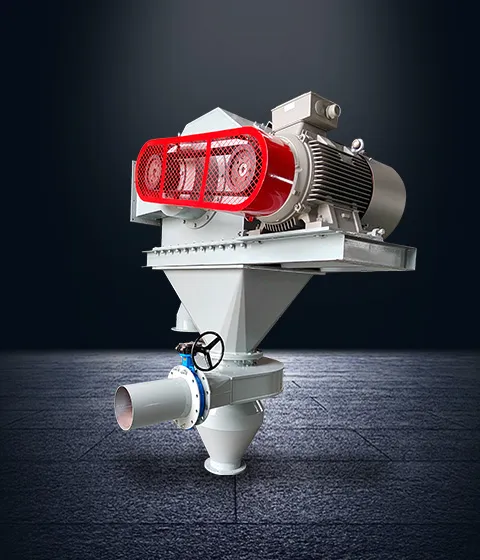

Centrifugal Classifier
The Centrifugal Classifier combines centrifugal force and gravity to separate metal powders based on density and particle size. It excels at handling high-density metals such as tungsten and molybdenum, offering ultra-fine micron and sub-micron level classification with high accuracy. Known for its stable structure and reliable operation, this type of classifier is widely used for hard alloys, high-temperature alloys, and electronic packaging materials.
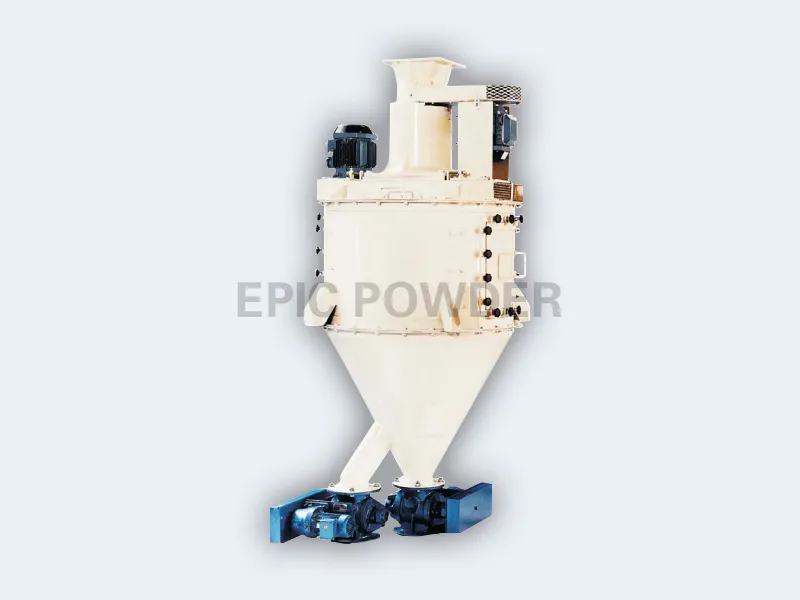

Inert Gas Protection Classifier
For highly reactive powders, the Inert Gas Protection Classifier performs classification within an inert atmosphere — such as nitrogen or argon — to prevent oxidation or combustion. This system ensures high safety while enabling ultra-pure classification free from contamination. It usually incorporates a fully enclosed circulation system to minimize gas consumption. This classifier is especially suitable for flammable metal powders like magnesium alloys, aluminum-lithium alloys, and titanium alloys.
Lastly, the Multi-Stage Integrated Classifier combines different classification technologies, such as air and centrifugal classification, in series or parallel to achieve extremely high precision and ultra-narrow particle size distributions. Though the equipment structure is more complex and costly, it’s ideal for applications requiring stringent particle size control, including semiconductor materials, advanced ceramics, and biomedical materials.
Selection Considerations
- Particle Size Requirements: Air classifiers are ideal for micron-level separation, while wet classifiers better handle nano-level classification.
- Material Properties: Reactive powders require inert gas protection, whereas high-density metals benefit from centrifugal classifiers.
- Production Scale: Multi-stage integrated classifiers suit large-scale production, while turbo classifiers fit smaller-scale experimental or pilot runs.
Epic Powder
Choosing the appropriate classifying equipment depends on balancing material characteristics, particle size goals, production volume, and budget. Epic Powder is dedicated to the research, development, and manufacturing of high-precision classification equipment. Our classifiers are engineered to deliver exceptional performance in terms of efficiency, accuracy, and reliability. They’re ideal for processing ultra-fine spherical metal powders across various high-end applications. Epic Powder provides tailored solutions that help customers achieve precise particle size distribution and outstanding product consistency.

